Connection Between Diabetes and Neuropathy
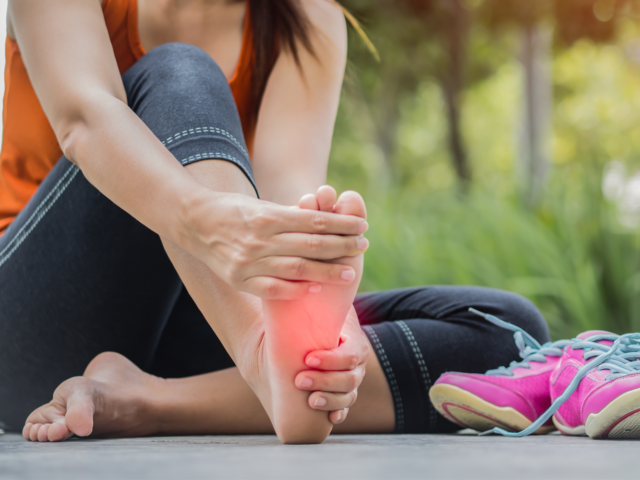

Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, affects millions of people worldwide. While most are aware of the potential complications related to diabetes, one aspect that requires more attention is the connection between diabetes and neuropathy. Neuropathy refers to nerve damage, which can result in a range of symptoms and complications. In this comprehensive 1500-word article, we will delve deep into the intricate relationship between diabetes and neuropathy, exploring causes, symptoms, prevention, and management.
Understanding Neuropathy in Diabetes
Neuropathy in diabetes, often referred to as diabetic neuropathy, is a prevalent and potentially debilitating complication of diabetes. It primarily affects the nerves in the legs and feet but can also involve other parts of the body. This condition occurs due to prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels, which can damage the delicate nerve fibers responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body.
The Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of diabetic neuropathy, including:
- Prolonged High Blood Sugar: Elevated glucose levels in the blood over an extended period are the primary cause of nerve damage in diabetes. This excess sugar can impair nerve function and lead to neuropathic symptoms.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation associated with diabetes can further exacerbate nerve damage. Inflammatory processes within the body can directly affect nerves, leading to neuropathic symptoms.
- Blood Vessel Damage: Diabetes can cause damage to blood vessels, reducing blood flow to nerves. Poor circulation deprives nerves of oxygen and essential nutrients, leading to nerve injury.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to neuropathy, making them more susceptible to its development, even with well-managed diabetes.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Diabetic neuropathy can manifest in various ways, depending on the type of nerves affected. Common symptoms include:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: This type affects the peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms such as tingling, numbness, burning sensations, and pain in the extremities, particularly the feet and legs.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Autonomic nerves control involuntary bodily functions. When damaged, they can lead to digestive issues, heart rhythm problems, and blood pressure fluctuations.
- Proximal Neuropathy: Also known as diabetic amyotrophy, this condition causes pain and weakness in the thighs, hips, or buttocks.
- Focal Neuropathy: Focal neuropathy typically affects a single nerve, leading to sudden weakness or pain in specific areas, such as the wrist or leg.
Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy
Prevention is key when it comes to diabetic neuropathy. Here are some strategies to reduce your risk:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is the most effective way to prevent neuropathy. Regular monitoring and adherence to your treatment plan are crucial.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Incorporating a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain overall health and reduce the risk of neuropathy.
- Foot Care: Proper foot hygiene and regular foot exams are essential for preventing complications in the lower extremities.
Managing Diabetic Neuropathy
If you’re already experiencing symptoms of diabetic neuropathy, it’s essential to manage the condition effectively. Here are some approaches:
- Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to alleviate pain and manage symptoms. These can include pain relievers, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making necessary adjustments to your daily life, such as wearing comfortable shoes, practicing good foot hygiene, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can significantly improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
The connection between diabetes and neuropathy is undeniable, and understanding this link is crucial for everyone living with diabetes. By taking proactive steps to control blood sugar levels and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing neuropathy or manage existing symptoms effectively.
In conclusion, diabetes is a challenging condition that requires comprehensive management, and neuropathy is one of its potential complications that should not be underestimated. By prioritizing your health and seeking regular medical check-ups, you can minimize the impact of diabetic neuropathy on your life. If you are seeking a source of inspiration and guidance about neuropathy, visit their page for further info.



